How Long Do Ants Live
hellogrow
on
February 24, 2024
Exploring the Lifespan of Ants:
The longevity of an ant is influenced by a myriad of factors, ranging from its species to its specific role within the colony’s social structure.
The most significant variable affecting an ant’s lifespan is its caste system, which dictates the duties an ant performs within its community.
This caste system is determined by genetic factors from the queen ant and the nurturing environment provided by worker ants, which includes feeding and caring for ant larvae. The queen ant plays a crucial role in this process by selectively fertilizing eggs, while worker ants cater to larvae’s nutritional needs, steering them towards their future roles within the colony.
Each caste within an ant colony experiences a different lifespan, with queen ants capable of living for decades under the right conditions.
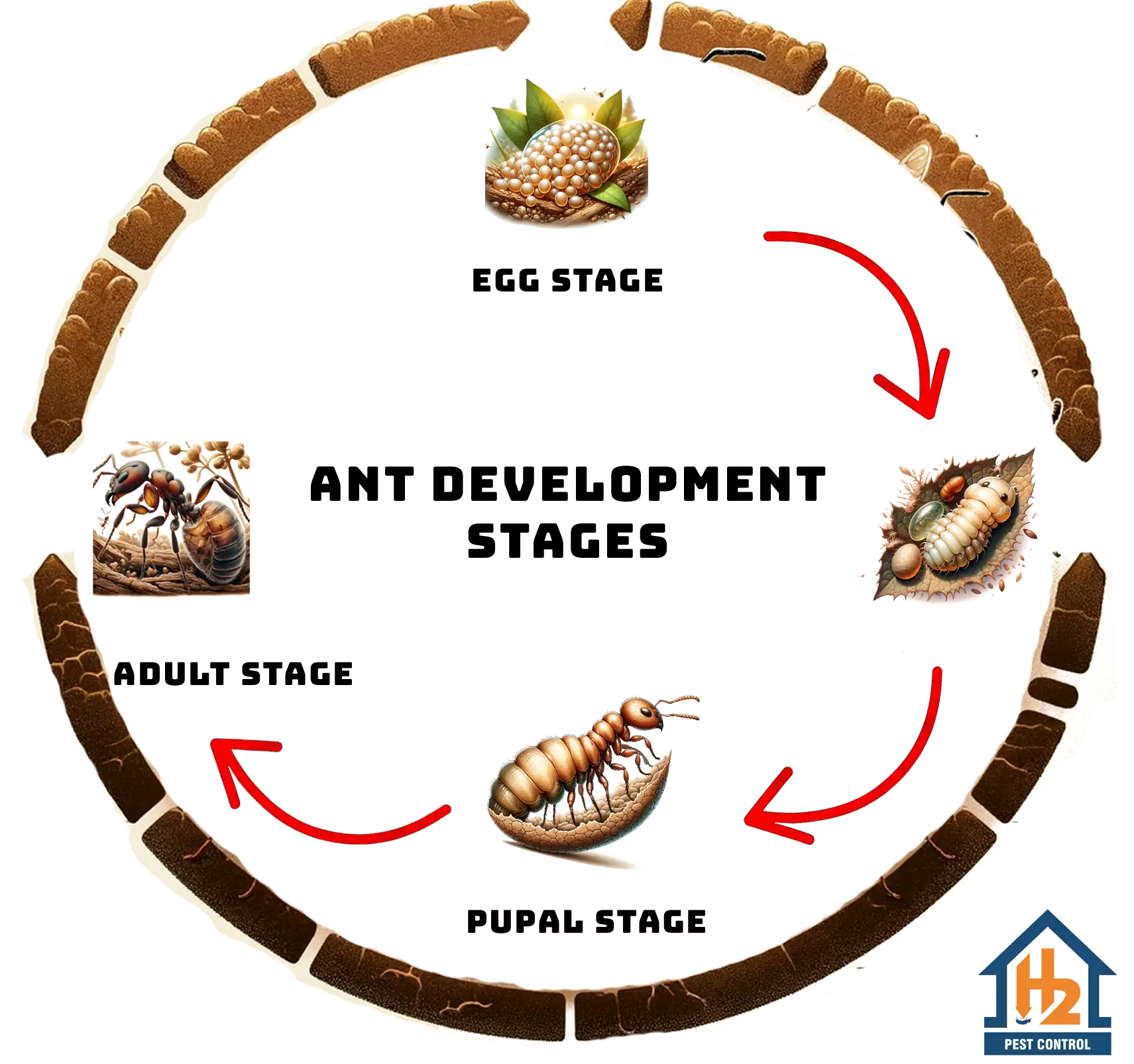
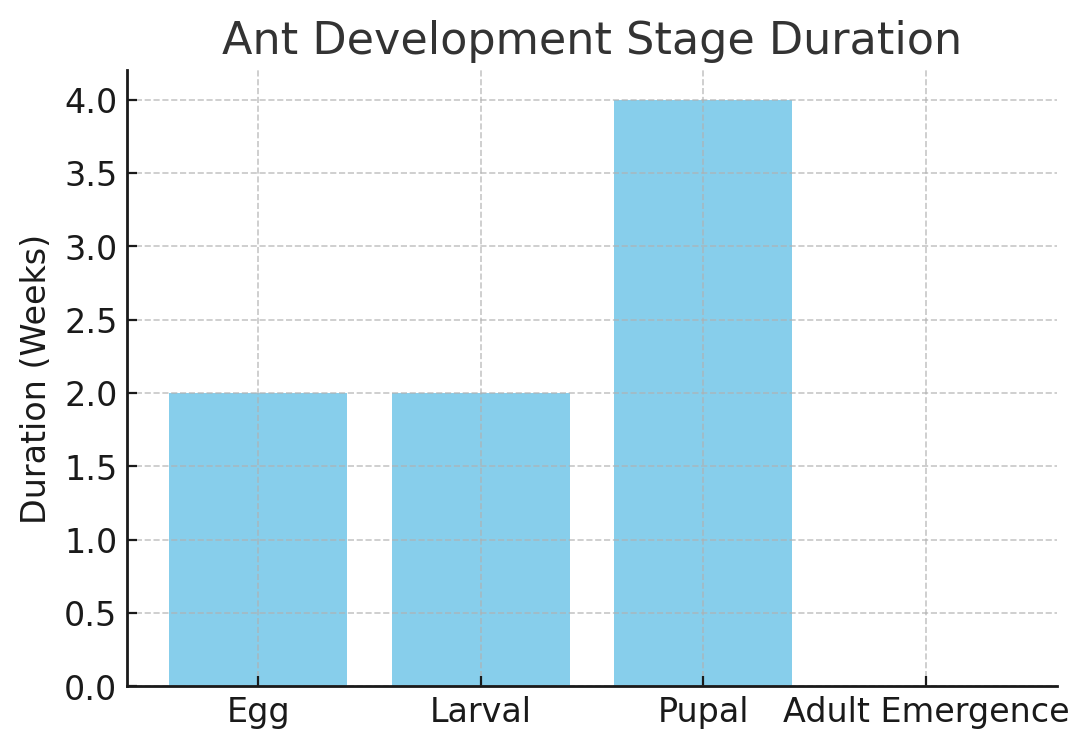
Egg Stage: The journey of an ant begins as an egg. This phase lasts about 1 to 2 weeks, during which the foundation for caste differentiation is laid. The queen’s selective fertilization decides whether an egg will develop into a female worker, soldier, or alate (future queen or male drone), with unfertilized eggs developing into male drones.
Larval Stage: Following the egg stage, ants enter the larval phase, characterized by their legless, blind state. Here, they rely entirely on worker ants for nourishment. Lasting 1 to 2 weeks, this stage is pivotal for caste differentiation, influenced by the diet and pheromonal exposure. A colony’s composition, typically 95% workers and 5% soldiers, is maintained through a balance of nutritional provisioning and pheromonal regulation.
Pupal Stage: The pupal stage marks the transition towards adulthood, with ants taking on the appearance of their mature form but remaining inactive. This stage can last from one to four weeks, culminating in the emergence of an adult ant ready to fulfill its role within the colony.
Adult Stage: Upon reaching adulthood, an ant assumes its role as a worker, soldier, drone, or alate, with its lifespan now subject to factors like environmental conditions and availability of resources.
Factors Influencing Ant Lifespans
Several elements play a role in determining the lifespan of ants:
-
Species: Lifespans vary significantly across ant species.
-
Gender: Male ants typically live for about a week post-maturity, as their primary function is to mate with queens. Female ants, constituting the majority of the colony, have longer lifespans, varying by caste and species.
-
Caste: The queen, workers, soldiers, and alates each have distinct lifespans, reflecting their roles within the colony.
-
Resources: The availability of food and water is crucial for colony survival, with scarcity leading to reduced lifespans.
-
Environment: The habitat’s suitability can greatly affect an ant’s survival, with adverse conditions shortening lifespans.
-
External Threats: Predators, environmental hazards, and human interventions can prematurely end an ant’s life.
Caste-Specific Lifespans
-
Queen Ants: Serve as the colony’s reproductive foundation, with some species’ queens living between 10 to 28 years.
-
Worker Ants: Form the majority of the colony, with lifespans ranging from a few months to several years, depending on species.
-
Soldier Ants: Often face early mortality due to their protective duties.
-
Drones and Alates: Drones live briefly after mating, while alates venture to establish new colonies.
Species Variations in Lifespan
Ant species exhibit diverse lifespans, with examples including:
-
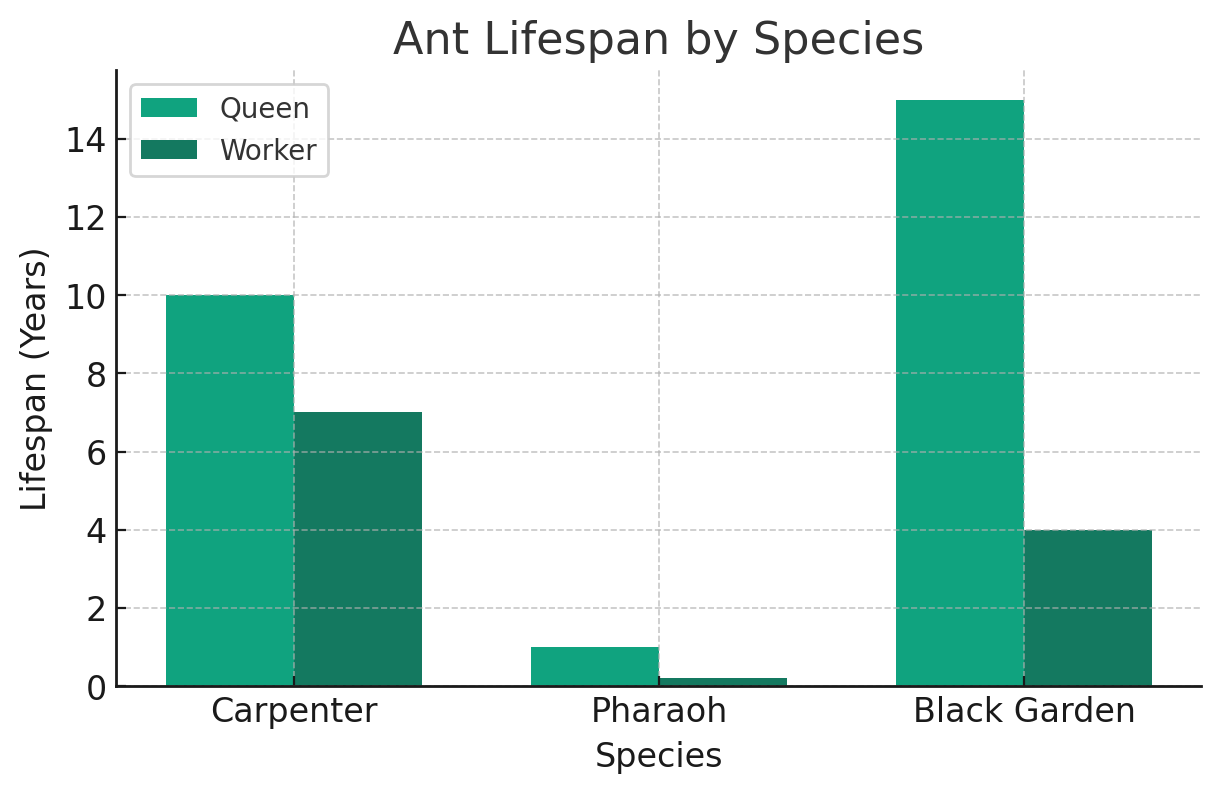
Carpenter Ant Workers: Up to 7 years
-
Pharaoh Ant Workers: Approximately 70 days
-
Black Garden Ant Queens: 15+ years
Sustenance and Survival
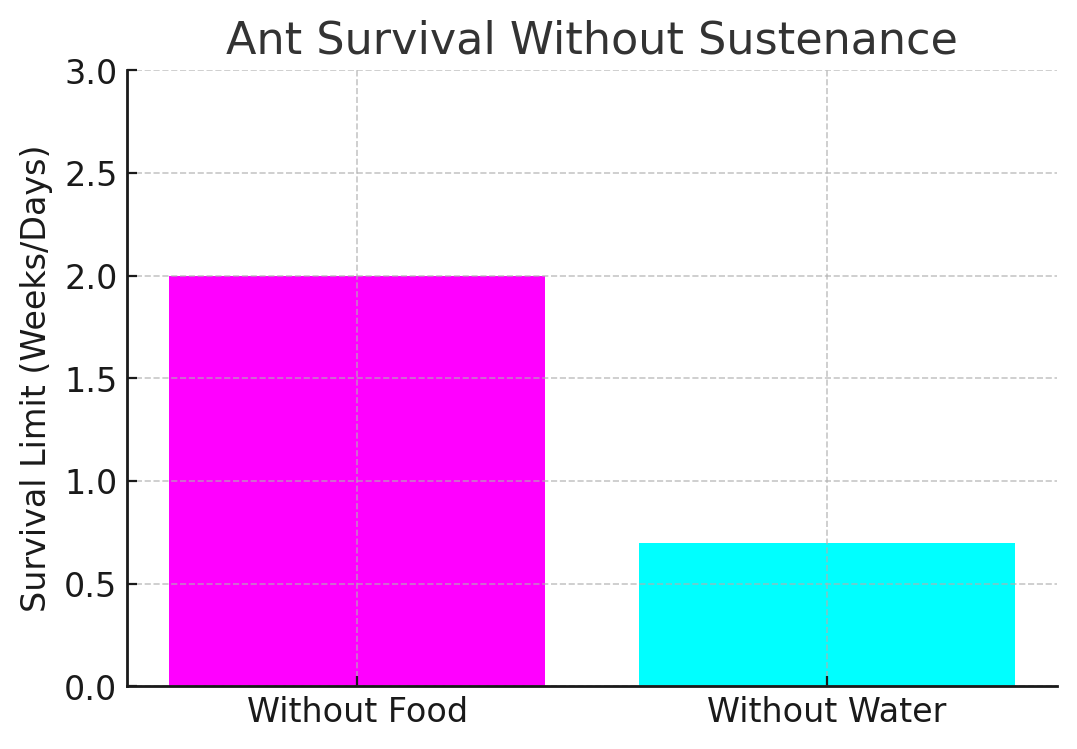
Ants’ ability to survive without food or water varies, with workers potentially lasting 1-2 weeks without food. Water deprivation studies suggest ants can survive around 5 days without hydration.
Seeking Professional Ant Control
If ant presence becomes a concern, professional extermination services like H2 Pest Control can offer solutions tailored to effectively address and prevent ant infestations.